Agronomist notebook: A step-by-step guide to effective herbicide use
SATURDAY MAY 16 2020
By ANN MACHARIA
Increased rains have caused rapid growth of weeds on farms, threatening crops.
Farmers, therefore, have to increase the frequency at which they eliminate the unwanted crops. While some uproot and others weed with hoes, an increasing number of farmers are using herbicides.
Arnold, a farmer in Nakuru, told me the other day he sprayed a herbicide to control blackjack and pigweeds on his maize farm but the chemical did not do much since soon after spraying, it rained heavily.
Some farmers have also complained that they sprayed herbicides to control weeds but instead, the chemicals scorched their crops.
In many cases, weeds can be easily managed by using cultural methods such as uprooting, mulching and planting a cover crop. However, more farmers are now turning to herbicides to reduce the cost of labour.
Ineffectiveness of a chemical always results in losses to a farmer since they have to incur extra costs. A weed normally competes for nutrients, light and space with the crop, resulting in reduced yields.
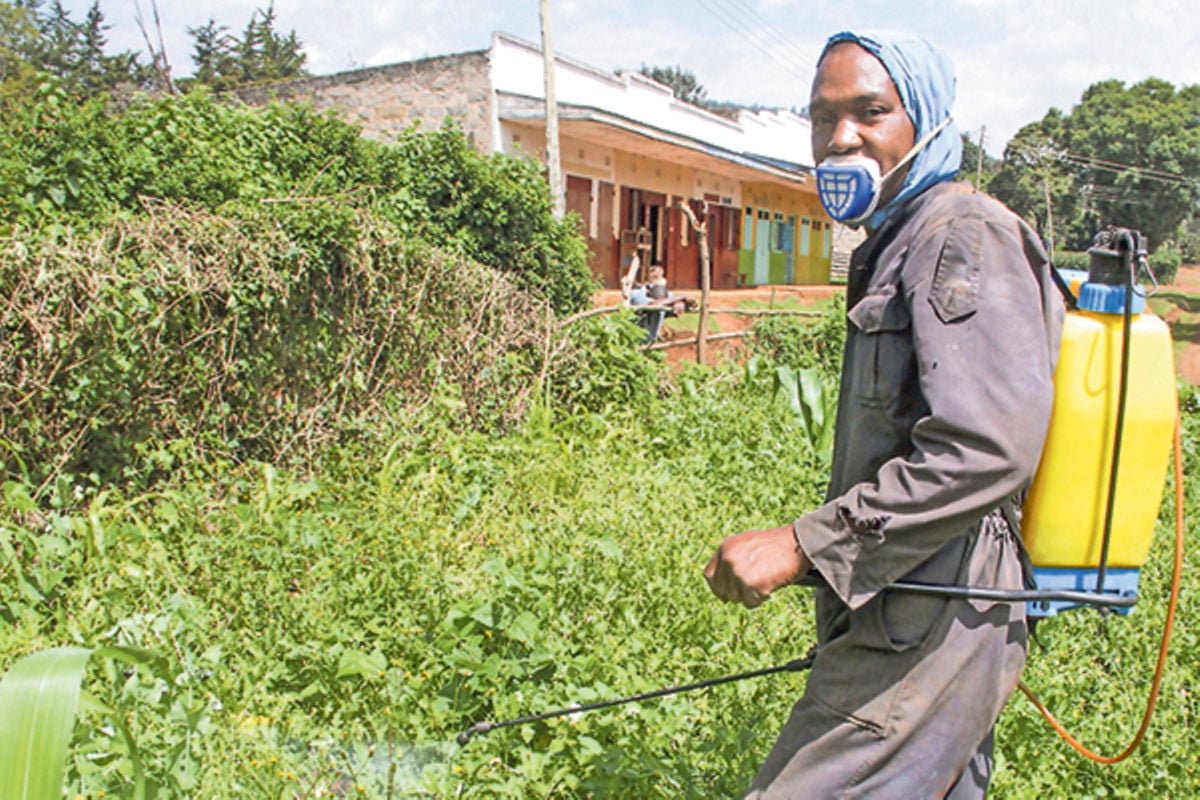
But how does one effectively use herbicides? Before you mix the chemicals, read the label instructions carefully so that you understand what needs to be done.
Check for the herbicide’s registration number with the Pest Control Products Board of Kenya to ensure that it is a genuine product.
Always identify the weeds and select the proper herbicides for the application site.
The label should list the weeds being controlled. In most cases, the herbicides will kill all susceptible plants and not just the weeds.
Also, consider the stage of the weeds. For instance, some chemicals are best applied before the weeds emerge (pre-emergence herbicides) and others after the plants develop (post-emergence). Pre-emergence herbicides control the germinating seeds before the weeds emerge from the soil.
USE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE
Post-emergence herbicides, on the other hand, control plants that have already emerged and are effective when the weeds are still young.
If clearing the land, use a non-selective herbicide to kill all the weeds. While the selective herbicides will kill the targeted weeds.
Avoid spraying during a rainy day as the rainwater will wash away or dilute the chemical, making it ineffective.
To avoid spills into unwanted places, one should avoid spraying in windy conditions. Use a spray guard to curb the chemical drift.
While spraying selective herbicides, avoid spraying to the crop directly as this may suppress its growth or scorch the plant being weeded.
Use the recommended dosage as indicated in the chemical label as excess may affect micro-organisms in the soil.
Using lower rates than recommended results in ineffectiveness.
Moist soils promote rapid plant growth, resulting in herbicide injury while too high temperatures result in degradation of the chemical, hence reducing its efficiency level.
Therefore, apply the herbicide during cool weather conditions.
Spray slightly above the plant and ensure good crop coverage, especially for contact herbicides. If the weeds are tall, it’s advisable to first slash the weeds and then spray to enhance chemical effectiveness.
Have separate knapsacks for the non-selective herbicides as the chemical residues may scorch the plant while spraying foliar or the pesticides.
After spraying, wash the knapsack thoroughly with clean water and properly dispose of the chemical residues.
All chemicals are poisonous if not used effectively. Therefore, while spraying, ensure you protect yourself by wearing personal protective equipment that include gloves, gumboots, respirators, goggles and overall.
In case of any spills or skin contact, rinse the affected part with clean running water. Dispose of the empty bottles properly after perforating them to avoid reuse.

 www.nation.co.ke
www.nation.co.ke
SATURDAY MAY 16 2020
By ANN MACHARIA
Increased rains have caused rapid growth of weeds on farms, threatening crops.
Farmers, therefore, have to increase the frequency at which they eliminate the unwanted crops. While some uproot and others weed with hoes, an increasing number of farmers are using herbicides.
Arnold, a farmer in Nakuru, told me the other day he sprayed a herbicide to control blackjack and pigweeds on his maize farm but the chemical did not do much since soon after spraying, it rained heavily.
Some farmers have also complained that they sprayed herbicides to control weeds but instead, the chemicals scorched their crops.
In many cases, weeds can be easily managed by using cultural methods such as uprooting, mulching and planting a cover crop. However, more farmers are now turning to herbicides to reduce the cost of labour.
Ineffectiveness of a chemical always results in losses to a farmer since they have to incur extra costs. A weed normally competes for nutrients, light and space with the crop, resulting in reduced yields.
But how does one effectively use herbicides? Before you mix the chemicals, read the label instructions carefully so that you understand what needs to be done.
Check for the herbicide’s registration number with the Pest Control Products Board of Kenya to ensure that it is a genuine product.
Always identify the weeds and select the proper herbicides for the application site.
The label should list the weeds being controlled. In most cases, the herbicides will kill all susceptible plants and not just the weeds.
Also, consider the stage of the weeds. For instance, some chemicals are best applied before the weeds emerge (pre-emergence herbicides) and others after the plants develop (post-emergence). Pre-emergence herbicides control the germinating seeds before the weeds emerge from the soil.
USE RECOMMENDED DOSAGE
Post-emergence herbicides, on the other hand, control plants that have already emerged and are effective when the weeds are still young.
If clearing the land, use a non-selective herbicide to kill all the weeds. While the selective herbicides will kill the targeted weeds.
Avoid spraying during a rainy day as the rainwater will wash away or dilute the chemical, making it ineffective.
To avoid spills into unwanted places, one should avoid spraying in windy conditions. Use a spray guard to curb the chemical drift.
While spraying selective herbicides, avoid spraying to the crop directly as this may suppress its growth or scorch the plant being weeded.
Use the recommended dosage as indicated in the chemical label as excess may affect micro-organisms in the soil.
Using lower rates than recommended results in ineffectiveness.
Moist soils promote rapid plant growth, resulting in herbicide injury while too high temperatures result in degradation of the chemical, hence reducing its efficiency level.
Therefore, apply the herbicide during cool weather conditions.
Spray slightly above the plant and ensure good crop coverage, especially for contact herbicides. If the weeds are tall, it’s advisable to first slash the weeds and then spray to enhance chemical effectiveness.
Have separate knapsacks for the non-selective herbicides as the chemical residues may scorch the plant while spraying foliar or the pesticides.
After spraying, wash the knapsack thoroughly with clean water and properly dispose of the chemical residues.
All chemicals are poisonous if not used effectively. Therefore, while spraying, ensure you protect yourself by wearing personal protective equipment that include gloves, gumboots, respirators, goggles and overall.
In case of any spills or skin contact, rinse the affected part with clean running water. Dispose of the empty bottles properly after perforating them to avoid reuse.

Agronomist notebook: A step-by-step guide to effective herbicide use
Always identify the weeds and select the proper chemicals for the application site
